Turbocharged diesel engines combine power and efficiency. Turbochargers for diesel engines improve performance, fuel efficiency, and vehicle life. Understanding turbochargers is essential for mechanics and car enthusiasts looking to improve their rides. This detailed guide will help you choose the right diesel turbocharger. We’ll cover turbocharger specifications, Garrett and ATS turbo models, turbo waste gates, and compressor maps. Prepare to turbocharge your diesel engine knowledge as we explore turbochargers.
Diesel Turbocharger Working Principle.
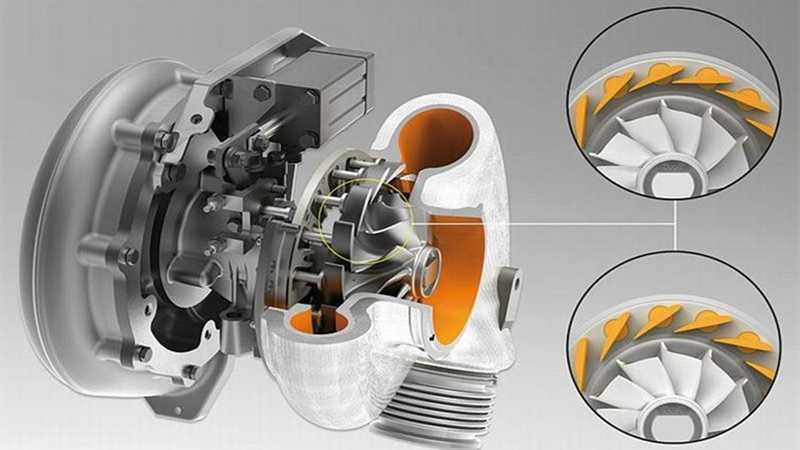
When buying a diesel engine turbocharger, you must understand its operation. Turbochargers use exhaust gases to boost engine power and efficiency.
Exhaust gases spin the turbocharger after leaving the engine. A shaft connects this turbine to an intake compressor. The compressor spins with the turbine. The compressor draws in and compresses outside air to increase its density before entering the engine’s combustion chamber.
Forced induction burns more fuel per engine cycle, increasing engine power. Diesel engine exhaust volumes and operating temperatures provide more energy to drive turbochargers, making them more effective.
The wastegate controls exhaust gas flow to the turbine in the turbocharger. Controlling boost pressure with the wastegate prevents the turbo from spinning too fast and causing damage.
Turbocharger specifications matter too. These include compressor and turbine wheel size, housing design, and bearing system. Each turbocharger specification affects performance and should be considered in light of your engine and performance goals.
Finally, turbochargers vary. Different Garrett or ATS turbos have different features and performance. Choosing the right diesel turbocharger requires understanding these differences.
A Comprehensive Guide To Turbocharger Selection.
Selecting a diesel turbocharger requires careful consideration of several factors. These include engine horsepower goals, vehicle use (daily driving, towing, racing, etc.), and engine displacement. The turbo should boost without overheating or pressurizing the engine.
Knowing Turbocharger Details
Turbocharger specs are complicated, but they’re essential for buying. The compressor wheel size and turbine housing A/R ratio affect how much air the turbo can move and how quickly it spools up. Other specs include journal or ball bearing, which affects durability and responsiveness, and internal or external wastegate, which controls boost pressure.
How To Buy A Turbocharger: Steps
1. Assess your needs: Determine your engine’s horsepower and vehicle use.
2. Know the specs: Learn how turbocharger specifications affect performance.
3. Compare choices: Compare specifications of turbochargers that meet your needs.
4. Purchase: After finding a turbo that meets your needs, buy from a trusted supplier.
5. Install: To avoid damage and maximize performance, have a professional install the turbocharger after purchase.
After following these steps and understanding the key factors and specifications, you can confidently choose a diesel turbocharger.
Maximizing Turbo Performance.
Several factors affect diesel turbo performance optimization. These include turbo inducer size, efficiency metrics like pounds-per-minute, road racing performance, and horsepower.
The turbine wheel diameter, or inducer size, affects a turbo’s performance. Airflow increases with inducer size, increasing power output. Larger turbos require more exhaust energy to spool up, which can slow response times (turbo lag).
Turbo efficiency metrics like lb/min measure air mass flow rate. This is crucial because more air pumped into the engine by a turbo increases fuel burning and power output. Thus, high-lb/min turbos perform better.
A turbo must provide consistent power across engine speeds for high-speed situations like road racing. This requires a well-balanced turbo with low-end response for corner acceleration and high-end power for straight-line speed.
Finally, turbo horsepower is important. This is the turbo’s horsepower limit. Larger, more efficient turbos with higher horsepower may not be suitable for all applications due to their slower response times.
Turbocharger Selection By Engine Type.
Choosing the right diesel turbocharger for your engine type can boost performance. Selecting a turbocharger kit and choosing compound turbos are important factors.
Consider several components when choosing a turbocharger kit. Make sure the kit includes a turbocharger that matches your engine’s displacement and power goals. A turbo manifold should be included to direct exhaust gases into the turbo. The turbo needs an inter cooler to cool compressed air, oil lines to lubricate it, and a downpipe to exhaust exhaust gases. The kit should also include installation hardware and gaskets.
In contrast, compound turbos use two turbochargers to boost power across the RPM range. First turbocharger, often smaller, provides quick response and low-end power, while second turbo boosts top-end power at higher RPMs. This setup is ideal for racing and heavy-duty applications that require maximum power and efficiency. Most are more complicated and expensive than single turbo setups.